Project 1: Math Tutor
Project 1.1
Participate in the lesson 7 discussion. This could involve asking a question, answering another student's question, giving an example of something that you struggled with and then overcame (or didn't!), giving an example of something you found particularly cool, or any other constructive way you can think of to participate.Project 1.2
Do Dale chapter 7 EPE 1 - 14. Write the answers neatly or type them up, and staple them to the back of this assignment. (Online students: type them up and paste them into your e-mail message.)Project 1.3
This program will ask the user to answer a series of arithmetic problems and report on how the user performs. You will write this program in the following phases. Make sure that each phase works correctly and is stylistically perfect before progressing to the following phase.
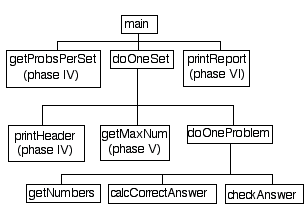
Note that the purpose of this assignment is to give you lots of practice with parameter passing without making you write a huge program. For this reason I have provided a structure diagram at the end of this document. Make sure that you adhere to the structure diagram carefully.
Turn in only your final product.Phase I: Your main function for phase I must look exactly like this:
int main() { srand(time(0)); doOneSet(); }
You must write the function doOneSet which will, for now, write out 5 addition problems. All of the numbers in your programs should be between 0 and 100. Here is the sample output for this phase:
45 + 21 = 0 + 100 = 54 + 23 = 4 + 19 = 18 + 92 =
The numbers that are produced for these problems must be generated randomly by the computer. The numbers in the sample output are given only as an example. We will discuss in the lessons how to generate random numbers.
Phase II: Change your doOneSet function so that instead of just writing out the problems it also allows the user to enter an answer, and then tells the user whether the answer was correct or not. Do not change your main function. Here is the sample output for this phase (user input is indicated here by using bold font. It won't be bold in your own output):
45 + 21 = 66 correct 0 + 100 = 100 correct 54 + 23 = 67 incorrect 4 + 19 = 13 incorrect 18 + 92 = 100 correct
Phase III: Now you will change your doOneSet function so that it will work for either addition, subtraction, or multiplication. For the purposes of this assignment, a set of problems is defined to be a group of problems that are all of the same type (all addition, all subtraction, or all multiplication). After completing this phase your program will give 5 addition problems, 5 subtraction problems, and 5 multiplication problems, for a total of 15 problems. Your main function must look exactly like this:
int main() { srand(time(0)); doOneSet('+'); doOneSet('-'); doOneSet('*'); }
The parameter tells doOneSet whether to do addition, subtraction, or multiplication. Notice that there is exactly one doOneSet function definition, not three! Here is the sample output for this phase:
45 + 21 = 66 correct 0 + 100 = 100 correct 54 + 23 = 67 incorrect 4 + 19 = 13 incorrect 18 + 92 = 100 correct 59 - 19 = 40 correct 19 - 84 = -29 incorrect 0 - 65 = -65 correct 96 - 1 = 95 correct 94 - 14 = 80 correct 0 * 87 = 0 correct 45 * 84 = 398 incorrect 8 * 37 = 873 incorrect 34 * 83 = 831 incorrect 38 * 3 = 238 incorrect
Note: Do not proceed on from phase III until you are sure your program is perfect and you have checked to make sure that you have adhered to structure diagram given at the end of this document!!!
Phase IV: Now you are ready to let the user specify how many problems per set. (Recall that a set is a group of problems all of the same type. In this program we are doing three sets: one set of addition, one set of subtraction, and one set of multiplication. This means that, for example, if the problems per set is 7, there will be a total of 21 problems given.) Ask the user to enter the number of problems per set at the very beginning of the program, so that all three sets have the same number of problems per set. Now your main function will look exactly like this (you may add variable declarations only):
int main() { srand(time(0)); getProbsPerSet(probsPerSet); doOneSet('+', probsPerSet); doOneSet('-', probsPerSet); doOneSet('*', probsPerSet); }
For this phase you should also add a header at the beginning of each set, as illustrated in the following sample output for this phase. For purposes of the header, you should assume that the addition problems will always be set #1, the subtraction problems set #2, and the multiplication problems set #3.
Enter problems per set: 3 Set #1 ---------- 45 + 21 = 66 correct 0 + 100 = 100 correct 54 + 23 = 67 incorrect Set #2 ---------- 59 - 19 = 40 correct 19 - 84 = -29 incorrect 0 - 65 = -65 correct Set #3 ---------- 0 * 87 = 0 correct 45 * 84 = 398 incorrect 8 * 37 = 873 incorrect
Phase V: Now let the user specify maxNum, the maximum number to be used for each set. This means that instead of choosing numbers between 0 and 100 (inclusive) for each problem, the computer will be choosing numbers between 0 and maxNum (inclusive). You must allow the user to enter a different maximum number for each set. This won't change the main function, since you need to ask it again before each set. It will be done near the beginning of your doOneSet function. Here's the sample screen output:
Enter problems per set: 3 Set #1 ---------- What is the maximum number for this set? 100 45 + 21 = 66 correct 0 + 100 = 100 correct 54 + 23 = 67 incorrect Set #2 ---------- What is the maximum number for this set? 90 59 - 19 = 40 correct 19 - 84 = -29 incorrect 0 - 65 = -65 correct Set #3 ---------- What is the maximum number for this set? 20 0 * 18 = 0 correct 15 * 4 = 398 incorrect 8 * 17 = 873 incorrect
Phase VI: Now you need to keep track of how the user is doing. At the end of the program, write a report which says how many the user got right on each set out of how many and for what percent. Also tell the overall figures. Here's the sample screen output:
Enter problems per set: 3 Set #1 ---------- What is the maximum number for this set? 100 45 + 21 = 66 correct 0 + 100 = 100 correct 54 + 23 = 67 incorrect Set #2 ---------- What is the maximum number for this set? 90 59 - 19 = 40 correct 19 - 84 = -29 incorrect 0 - 65 = -65 correct Set #3 ---------- What is the maximum number for this set? 20 0 * 18 = 0 correct 15 * 4 = 398 incorrect 8 * 17 = 873 incorrect Set#1: You got 2 correct out of 3 for 67% Set#2: You got 2 correct out of 3 for 67% Set#3: You got 1 correct out of 3 for 33% Overall you got 5 correct out of 9 for 56%
Your main function for phase VI must look like this (you may add variable declarations and arguments only):
int main() { srand(time(0)); getProbsPerSet(<arguments>); doOneSet(<no-more-than-3-arguments>); doOneSet(<no-more-than-3-arguments>); doOneSet(<no-more-than-3-arguments>); printReport(<arguments>); }
Please note that you may send no more than 3 arguments to doOneSet. Hint: Although main will need three separate variables to keep track of the number of problems answered correctly in each set, your doOneSet function will have only one parameter which keeps track of the number of problems answered correctly in the current set. It will be up to main to get that information into the correct variable.
The following structure diagram includes every function that you will have in your program. You should have no more and no fewer, and you should use the names that have been suggested here. Functions pictured below that are not labeled with a phase should be implemented at least by phase III. Please also read the notes below the structure diagram very carefully.
Notes:
- Note: The doOneProblem function does exactly one problem, not one *type* of problem!!
- Please change getNumbers to generateOperands
- CheckAnswer is the function that writes either "correct" or "incorrect"
- You will receive a 0 on this assignment if you use global variables, arrays or structs
- Turn in only phase VI, your final product. Provide sample output.
You will lose points if the code you put in one of your functions does not correspond to the name of the function given in the structure diagram.
Turn in your source code for phase VI followed by your output from phase VI. A single output is sufficient.